Diabet: A Step-by-Step Guide to Balanced Daily Habits
Living with diabetes requires a proactive approach. It involves a delicate balance of various factors. This includes diet, exercise, medication, and regular monitoring. This comprehensive guide offers a step-by-step approach. It helps individuals with diabetes establish balanced daily habits. These habits are essential for effective diabetes management and overall well-being.
Understanding Diabetes and Its Impact
Diabetes is a chronic metabolic disorder. It is characterized by elevated blood sugar levels. There are several types of diabetes. The most common are Type 1 and Type 2. Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune disease. The body attacks and destroys insulin-producing cells. Type 2 diabetes is more prevalent. It often develops due to insulin resistance. The body struggles to use insulin effectively. This leads to high blood sugar.
Uncontrolled diabetes can lead to serious complications. These include heart disease, kidney damage, nerve damage, and vision loss. Managing diabetes effectively is crucial. It can significantly reduce the risk of these complications. It improves the quality of life.
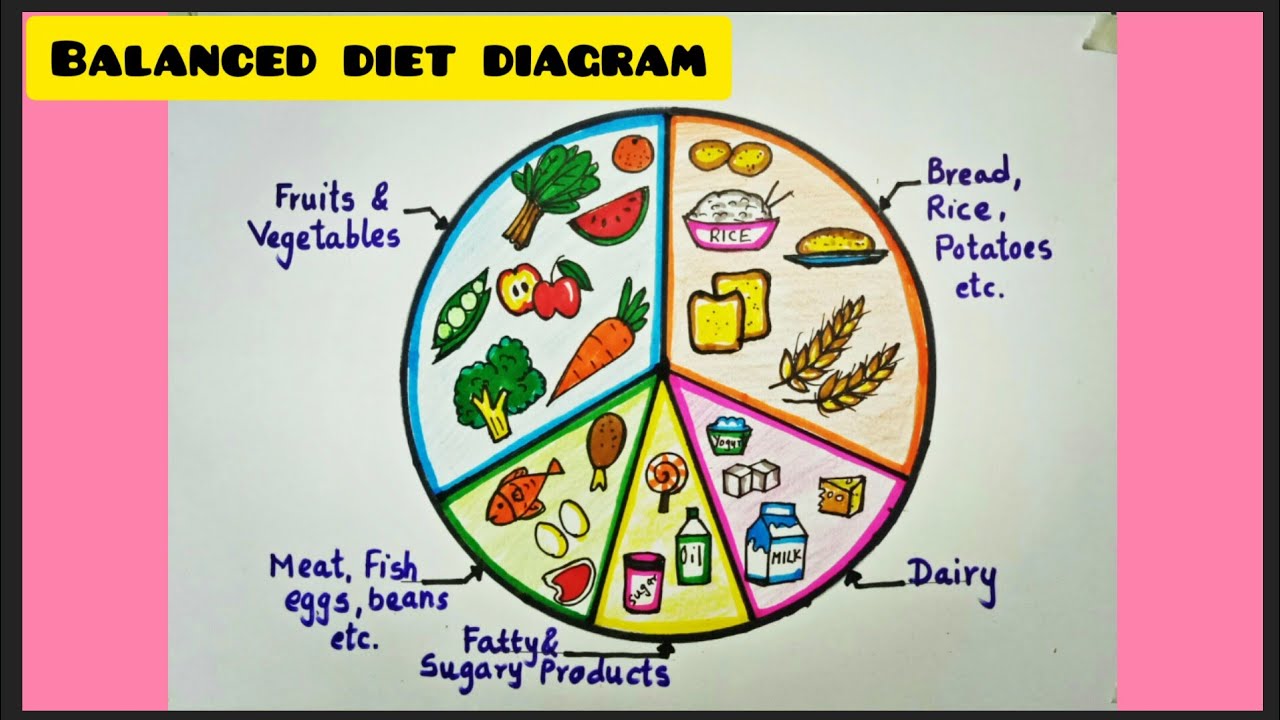
Step One: Nutrition and Meal Planning
Diet plays a central role in managing diabetes. The goal is to maintain stable blood sugar levels. This is achieved by making informed food choices. A registered dietitian or certified diabetes educator can provide personalized guidance. They tailor a plan to individual needs. Here are key aspects of nutrition and meal planning:
- Carbohydrate Counting: Understanding carbohydrate intake is vital. Carbohydrates affect blood sugar the most. Learn to count carbohydrates in meals and snacks. This helps to manage glucose levels effectively.
- Portion Control: Be mindful of portion sizes. Overeating can cause blood sugar spikes. Use smaller plates and measure food to control portions.
- Balanced Meals: Aim for balanced meals. Combine carbohydrates with protein and healthy fats. This slows down glucose absorption. It provides sustained energy.
- Choose Fiber-Rich Foods: Fiber helps regulate blood sugar. It promotes digestive health. Include plenty of non-starchy vegetables, fruits, and whole grains in your diet.
- Limit Processed Foods and Sugary Drinks: These foods and drinks can cause rapid blood sugar spikes. Avoid or minimize intake. Focus on whole, unprocessed foods.
- Hydration: Drink plenty of water. Water helps with kidney function and overall health. Avoid sugary drinks.
Step Two: Regular Physical Activity
Exercise is a powerful tool in diabetes management. It improves insulin sensitivity. It helps the body use insulin more effectively. This leads to better blood sugar control. It also offers other health benefits. It can reduce the risk of heart disease. It aids in weight management. Start slowly. Gradually increase the intensity and duration of exercise. Consult with a healthcare provider before starting any new exercise program. Here are exercise tips:
- Choose Activities You Enjoy: Find activities you enjoy. This increases the likelihood of sticking with the exercise routine. Consider walking, swimming, cycling, or dancing.
- Aim for at Least 150 Minutes of Moderate-Intensity Exercise Per Week: This can be broken down into shorter sessions. For example, 30 minutes of exercise, five days a week.
- Include Strength Training: Strength training helps build muscle mass. Muscle helps improve insulin sensitivity. Aim for strength training exercises at least twice a week.
- Monitor Blood Sugar: Check blood sugar levels before, during, and after exercise. This helps you understand how exercise affects your levels. Adjust your insulin or food intake as needed.
- Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of water before, during, and after exercise. Dehydration can affect blood sugar levels.
Step Three: Medication Management
Many individuals with diabetes require medication. It helps manage blood sugar levels. This could include oral medications or insulin. It is crucial to take medications as prescribed. Regular communication with your healthcare provider is essential. They monitor and adjust medications as needed. Here is a guide to effective medication management:
- Take Medications as Prescribed: Follow the dosage instructions carefully. Do not skip doses. Do not change the dosage without consulting your doctor.
- Understand Your Medications: Learn about the purpose of each medication. Know the potential side effects. Ask your healthcare provider any questions.
- Store Medications Properly: Store medications according to instructions. This ensures their effectiveness. Keep them out of reach of children.
- Monitor Blood Sugar Regularly: Regular blood sugar monitoring helps you assess your medication’s effectiveness. It helps you identify any problems.
- Keep a Medication Log: Keep a log of the medications you take. Include the dosage and time. This helps you track your medication schedule. It helps you identify any missed doses.
- Refill Prescriptions on Time: Ensure you have enough medication. Avoid running out of medications. Set reminders to refill prescriptions on time.
Step Four: Blood Glucose Monitoring
Regular blood glucose monitoring is essential. It provides valuable information about blood sugar levels. It helps you make informed decisions about your diet, exercise, and medication. It allows you to adjust your habits as needed. Here are key aspects of blood glucose monitoring:
- Test Your Blood Sugar Regularly: Follow your healthcare provider’s recommendations. They specify how often to test your blood sugar. This depends on your treatment plan.
- Use a Blood Glucose Meter Correctly: Follow the instructions for your blood glucose meter. This will ensure accurate results.
- Record Your Results: Keep a log of your blood sugar readings. Record the time of day. Note any meals, snacks, or exercise.
- Identify Patterns: Look for patterns in your blood sugar readings. They help you understand how your habits affect your levels.
- Share Results with Your Healthcare Provider: Share your blood sugar readings with your healthcare provider. They can assess your diabetes management. They can make any necessary adjustments.
- Understand Target Ranges: Know your target blood sugar ranges. This helps you interpret your readings. It helps you take appropriate actions.
Step Five: Stress Management and Mental Health
Diabetes can be stressful. Stress affects blood sugar levels. It is important to manage stress and prioritize mental health. This improves overall well-being. It supports effective diabetes management. Here are stress management tips:
- Practice Relaxation Techniques: Try relaxation techniques. These include deep breathing, meditation, or yoga. These can help reduce stress. They can improve your mood.
- Get Enough Sleep: Aim for seven to eight hours of sleep each night. Lack of sleep can increase stress levels. It can negatively impact blood sugar control.
- Seek Social Support: Talk to friends, family, or a support group. Sharing your feelings can help reduce stress. It can provide emotional support.
- Engage in Hobbies: Make time for activities you enjoy. Hobbies can reduce stress. They can improve your overall well-being.
- Consider Therapy: If you are struggling with stress or mental health issues, consider therapy. A therapist can provide support. They can teach coping strategies.
Step Six: Regular Healthcare Check-ups
Regular check-ups with your healthcare team are essential. They monitor your overall health. This includes your diabetes management. These check-ups allow for early detection of complications. They allow for timely interventions. Here is a guide to regular healthcare check-ups:
- Visit Your Doctor Regularly: Schedule regular check-ups with your primary care physician. They monitor your overall health. They assess your diabetes management.
- See an Endocrinologist: An endocrinologist specializes in diabetes. They can provide specialized care. They can help with medication management.
- Get Regular Eye Exams: Diabetes can affect your vision. Schedule regular eye exams with an ophthalmologist or optometrist.
- See a Podiatrist: Diabetes increases the risk of foot problems. See a podiatrist regularly for foot exams and care.
- Get Vaccinations: Stay up-to-date on recommended vaccinations. This helps prevent infections. Infections can affect blood sugar levels.
- Monitor Kidney Function: Get regular kidney function tests. Diabetes can damage the kidneys. Early detection and treatment are crucial.
- Monitor Heart Health: Monitor your heart health. Diabetes increases the risk of heart disease. Get regular check-ups. Follow your doctor’s recommendations.
Step Seven: Education and Support
Education and support are vital for effective diabetes management. Learn as much as possible about diabetes. Seek support from healthcare professionals, support groups, and online resources. Here is a guide to education and support:
- Attend Diabetes Education Classes: These classes provide valuable information about diabetes. They teach you how to manage your condition.
- Read Reliable Information: Read books, articles, and websites. Choose reputable sources. Learn about diabetes management.
- Join a Support Group: Connect with other people with diabetes. Share experiences. Offer mutual support.
- Talk to Your Healthcare Team: Ask your healthcare team questions. They provide guidance. They offer support.
- Use Online Resources: Explore online resources. These include websites and apps. They provide information. They offer tools for diabetes management.
Step Eight: Monitoring and Adjusting
Diabetes management is an ongoing process. It requires regular monitoring. It needs adjustments. The goal is to maintain optimal health. This is achieved by evaluating your habits. You need to make changes as needed. Here are key points for monitoring and adjusting:
- Review Your Progress Regularly: Review your blood sugar readings. Review your medication. Review your exercise routine. Review your diet. Assess your progress.
- Identify Challenges: Identify any challenges. Identify any areas for improvement. This could include blood sugar control. This could include adherence to your treatment plan.
- Make Adjustments: Make adjustments to your diet, exercise, or medication. This should be done in consultation with your healthcare provider.
- Stay Flexible: Be prepared to adjust your habits. Diabetes management is not a one-size-fits-all approach. It requires flexibility.
- Celebrate Successes: Acknowledge and celebrate your successes. This can help you stay motivated. It can maintain your commitment.
Following these steps provides a solid foundation. These steps help individuals with diabetes. They empower them to take control of their health. This comprehensive approach emphasizes the importance of balanced daily habits. These habits contribute to effective diabetes management. They promote overall well-being. Remember that consistency and perseverance are key. Living with diabetes is manageable. It is achievable with dedication and the right support. Following this Diabet step-by-step guide helps you to achieve the best possible outcomes. This Diabet guide is designed to help you live a fulfilling life. Make sure you consult with your healthcare provider. This Diabet guide provides general information. It is not a substitute for professional medical advice. This Diabet guide should enable you to live a healthy life. This Diabet guide is designed to help you. You can live a long and healthy life with Diabet. With Diabet, you can manage your condition effectively. Following this Diabet guide helps you achieve your health goals. The Diabet guide provides valuable insights. The Diabet step-by-step guide is a valuable tool. This Diabet step-by-step approach is a great resource. This Diabet guide provides a clear pathway. With Diabet, you can improve your quality of life. This Diabet guide offers a wealth of information.
[See also: Understanding Diabetes Complications]