Diabetes Home Monitoring Tips Experts Recommend: Staying Ahead of the Curve
Managing diabetes is a lifelong commitment. It demands constant vigilance and proactive measures. Effective diabetes management hinges on several key practices. One of the most crucial is consistent home monitoring. This article delves into the diabetes home monitoring tips experts recommend. We’ll explore best practices, equipment, and strategies. The goal is to empower individuals with diabetes to take control of their health. This helps them lead fulfilling lives.
Understanding the Importance of Home Monitoring
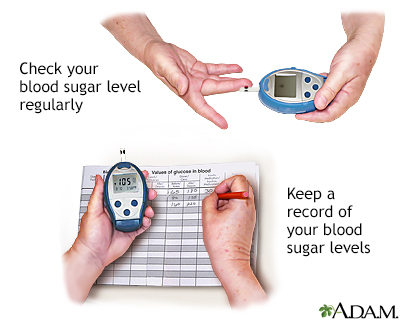
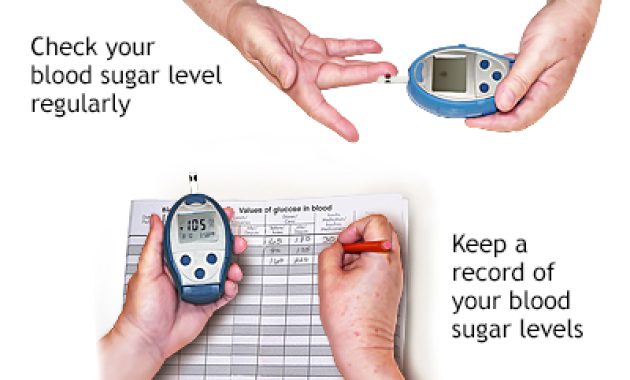
Regular blood glucose monitoring is the cornerstone of diabetes management. It provides invaluable insights into how diet, exercise, and medication affect blood sugar levels. This information helps individuals and their healthcare teams make informed decisions. They can adjust treatment plans as needed. This proactive approach can help prevent complications. These include cardiovascular disease, nerve damage, and kidney disease. Home monitoring isn’t just about numbers. It’s about understanding your body. It is about making informed choices to live well with diabetes.
Essential Equipment for Effective Monitoring
The tools of the trade for home monitoring have evolved. Modern technology has made the process easier and more accessible. Here’s a look at the essential equipment:
- Blood Glucose Meter: This is the core of home monitoring. It measures blood glucose levels from a small blood sample. Modern meters offer features like memory storage and data analysis. This helps track trends.
- Test Strips: These are single-use strips that react with blood glucose. They are inserted into the meter. They provide a reading of blood sugar levels. Ensure you use the correct strips for your meter.
- Lancing Device and Lancets: A lancing device creates a small puncture in the skin. This draws a blood sample. Lancets are single-use needles. They must be disposed of safely.
- Continuous Glucose Monitor (CGM): CGMs are advanced devices. They continuously track glucose levels throughout the day and night. They transmit data wirelessly to a receiver or smartphone. CGMs can alert users to high or low glucose levels.
- Insulin Delivery Devices (if applicable): These include insulin pens and insulin pumps. They help deliver insulin doses as prescribed.
Expert Tips for Accurate Blood Glucose Monitoring
Accuracy is paramount in home monitoring. Inaccurate readings can lead to incorrect treatment decisions. This can be harmful. Following these expert tips ensures the most reliable results:
- Wash Your Hands: Always wash your hands with warm, soapy water. Rinse thoroughly. Dry them completely. This removes any food particles or residue. This prevents inaccurate readings.
- Use Fresh Test Strips: Check the expiration date on your test strips. Use only fresh, unexpired strips. Store them properly. This is usually in a cool, dry place.
- Proper Lancing Technique: Use the lancing device on the side of your fingertip. This minimizes pain. Adjust the lancing depth. This ensures you get a sufficient blood sample.
- Apply Enough Blood: Ensure the test strip is fully saturated with blood. Insufficient blood can lead to inaccurate readings.
- Follow Meter Instructions: Each meter has specific instructions. Read and follow them carefully. This includes how to insert the strip and apply the blood.
- Record Your Readings: Keep a log of your blood glucose readings. Include the date, time, and any relevant factors. This could be food intake or exercise. This information is crucial for tracking trends.
- Calibrate CGMs: If using a CGM, calibrate it as instructed. This is usually done by taking a finger-prick blood glucose reading. This is to compare with the CGM reading.
- Check for Control Solutions: Use control solutions periodically. These are to test the meter’s accuracy. They confirm it’s functioning correctly.
Interpreting Your Blood Glucose Readings
Understanding your blood glucose readings is critical. It helps you make informed decisions. It also helps you manage your diabetes effectively. Here’s a guide to interpreting the numbers:
- Target Ranges: Your healthcare provider will establish target blood glucose ranges. These are based on your individual needs. These ranges generally vary. They depend on factors like age, overall health, and type of diabetes.
- Fasting Blood Glucose: This is the blood glucose level after an overnight fast. The target range is usually between 80-130 mg/dL.
- Pre-Meal Blood Glucose: This is the blood glucose level before a meal. It is typically between 80-130 mg/dL.
- Post-Meal Blood Glucose: This is the blood glucose level two hours after a meal. The target is usually less than 180 mg/dL.
- Hypoglycemia: This is low blood sugar. Symptoms include shakiness, sweating, and confusion. A blood glucose reading below 70 mg/dL is generally considered hypoglycemia. Treat it immediately with fast-acting carbohydrates.
- Hyperglycemia: This is high blood sugar. Symptoms include increased thirst and frequent urination. A blood glucose reading above 180 mg/dL can indicate hyperglycemia. Contact your healthcare provider if it persists.
- A1C: This test measures your average blood glucose levels over two to three months. It gives a broader picture of your diabetes management. The target A1C level is generally below 7%.
Lifestyle Factors and Home Monitoring
Lifestyle plays a huge role in diabetes management. It directly impacts blood glucose levels. Home monitoring helps you understand these relationships. Here’s how lifestyle factors interact with monitoring:
- Diet: What you eat has a direct impact on your blood sugar. Monitor blood glucose before and after meals. This helps you understand the impact of different foods. Work with a registered dietitian. They can help you create a meal plan. This is tailored to your needs.
- Exercise: Physical activity can lower blood sugar. Monitor blood glucose before, during, and after exercise. This helps you avoid hypoglycemia. This is especially important for people taking insulin or certain medications.
- Medication: Your medications play a crucial role in controlling blood sugar. Monitor your blood glucose regularly. This ensures your medications are effective. Work with your doctor. They can adjust your medication as needed.
- Stress: Stress can raise blood sugar levels. Monitor your blood glucose. This helps you understand the impact of stress. Learn stress management techniques. These include relaxation exercises and mindfulness.
- Sleep: Poor sleep can affect blood sugar. Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep each night. Monitor your blood glucose. This helps you understand the impact of sleep.
When to Seek Professional Guidance
Home monitoring is essential. It is not a substitute for professional medical care. There are times when you should seek guidance from your healthcare team:
- Persistent High or Low Blood Sugar: If your blood sugar levels are consistently outside your target range, consult your doctor. They can adjust your treatment plan.
- Changes in Symptoms: If you experience new or worsening symptoms of diabetes, seek medical attention.
- Illness or Infection: Illness can affect blood sugar levels. Monitor more frequently. Contact your doctor if you have concerns.
- Medication Adjustments: Any changes to your medication regimen require close monitoring. Consult your doctor.
- New Symptoms: If you experience new symptoms, such as vision changes or tingling in your extremities, consult your doctor immediately.
- Pregnancy: If you are pregnant or planning to become pregnant, consult your doctor. They will provide specialized guidance.
Continuous Glucose Monitoring: A Deeper Dive
Continuous Glucose Monitors (CGMs) offer a significant advantage in diabetes management. They provide real-time glucose readings. They also offer valuable insights into glucose trends. Here’s a closer look:
- How CGMs Work: A small sensor is inserted under the skin. It measures glucose levels in the interstitial fluid. The sensor transmits data to a receiver or smartphone.
- Benefits of CGMs: CGMs provide continuous data. They help identify trends. They also detect high and low glucose levels. This allows for proactive adjustments.
- Types of CGMs: There are various CGM systems available. They vary in features, such as accuracy and duration of wear.
- Integrating CGMs into your routine: Work with your doctor. They can help you integrate a CGM. This will optimize your diabetes management.
The Role of Technology in Home Monitoring
Technology is transforming diabetes home monitoring. It is offering new tools and insights. This empowers individuals. It also improves diabetes management. Here’s how technology is making a difference:
- Smart Meters: Many blood glucose meters now connect to smartphones. They allow for data upload and analysis.
- Diabetes Apps: Numerous apps help track blood glucose, food intake, and exercise. They also provide insights and reminders.
- Telehealth: Telehealth allows for remote consultations with healthcare providers. This facilitates remote diabetes management.
- Data Analysis Tools: These tools help analyze data from meters and CGMs. They identify patterns. They help personalize treatment plans.
Staying Motivated and Consistent
Managing diabetes requires ongoing effort and dedication. Staying motivated is crucial. Here are some tips to maintain consistency:
- Set Realistic Goals: Break down your goals into smaller, achievable steps. This makes the process less overwhelming.
- Find Support: Join a diabetes support group. Connect with other people with diabetes. Share experiences and learn from each other.
- Celebrate Successes: Acknowledge and celebrate your achievements. This reinforces positive behaviors.
- Stay Informed: Keep up-to-date with the latest advances in diabetes management. This empowers you with knowledge.
- Work with a Healthcare Team: Build a strong relationship with your healthcare providers. They can provide guidance and support.
Conclusion: Embracing a Proactive Approach
Diabetes home monitoring is a powerful tool. It empowers individuals. It helps them manage their condition effectively. By following the diabetes home monitoring tips experts recommend, you can take control. You can also improve your health. This helps you live a fulfilling life. Remember to stay informed. Consult with your healthcare team. Be proactive in your diabetes management journey. This is key to a healthy future. [See also: Diabetes Diet Plans for Beginners] [See also: Best Exercise for Diabetes Patients] [See also: How to Manage Diabetes During Travel]