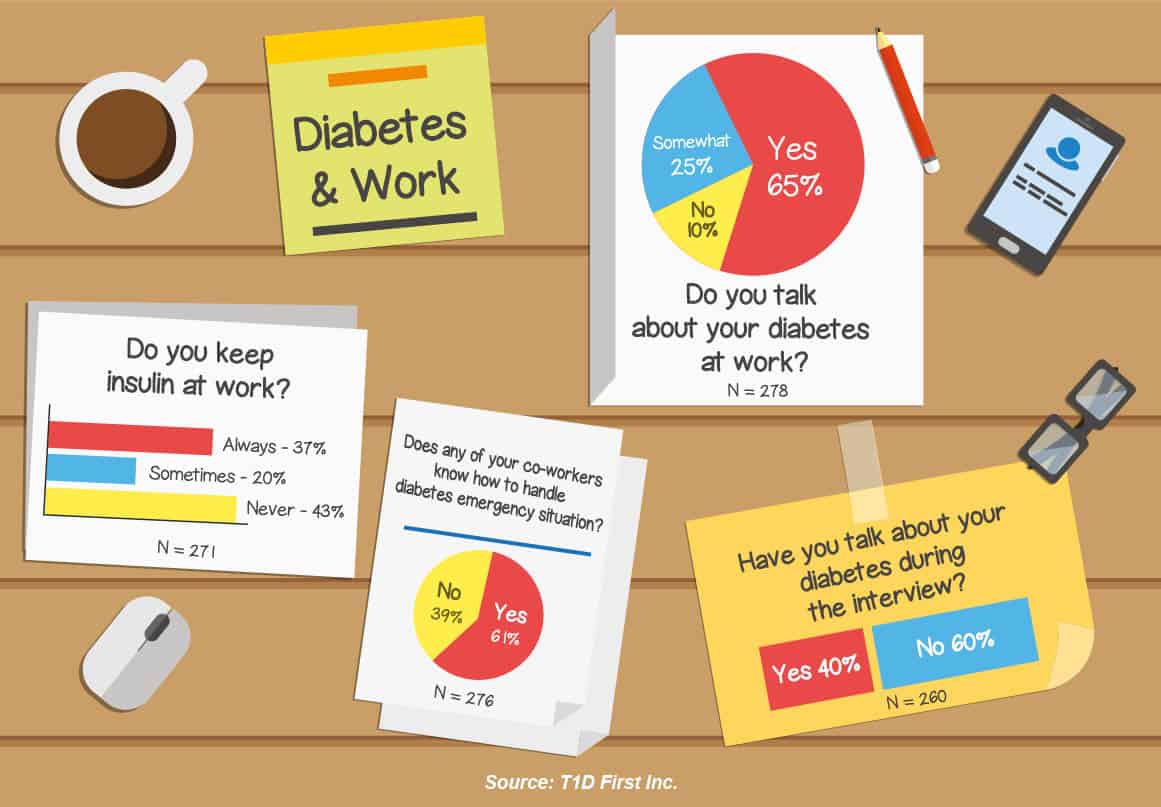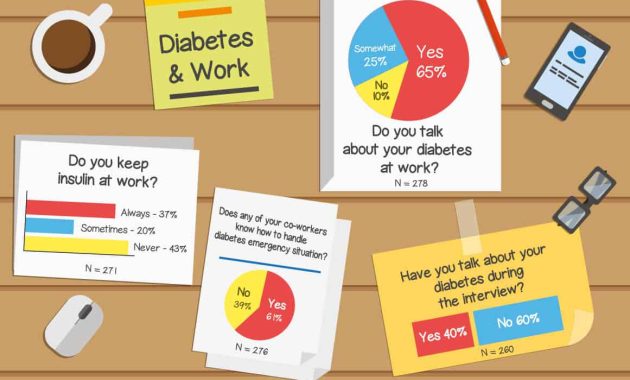
Diabetes at Work: A Guide to Sustained Productivity
The modern workplace demands peak performance. Yet, for individuals managing diabetes, navigating the demands of a job while maintaining stable blood sugar levels can be a significant challenge. The daily grind, long hours, and inherent stresses of work can disrupt glucose control. This can lead to energy crashes, reduced concentration, and ultimately, diminished productivity. However, with the right strategies and support, individuals with diabetes can thrive professionally. This article explores practical approaches to managing diabetes at work, ensuring sustained productivity, and achieving overall well-being.
Understanding the Challenges of Diabetes in the Workplace
Diabetes is a chronic condition affecting how the body processes glucose. This can lead to various complications if not managed effectively. The workplace environment can exacerbate these challenges. Inconsistent meal schedules, stress, and lack of opportunities for physical activity can all negatively impact blood sugar levels. Furthermore, the symptoms of high or low blood sugar, such as fatigue, irritability, and difficulty concentrating, can significantly impair job performance. These fluctuations can lead to missed deadlines, poor decision-making, and increased risk of errors.
The Impact of Hypoglycemia (Low Blood Sugar)
Hypoglycemia, or low blood sugar, is a common concern for people with diabetes. It can occur rapidly and lead to various symptoms. These include shakiness, sweating, confusion, and even loss of consciousness. In a work setting, these symptoms can be particularly dangerous. They can impair a person’s ability to operate machinery, drive, or make critical decisions. Regular monitoring of blood sugar levels is essential to prevent and manage hypoglycemic events. Carrying fast-acting carbohydrates, such as glucose tablets or juice, is crucial for treating hypoglycemia promptly.
The Effects of Hyperglycemia (High Blood Sugar)
Hyperglycemia, or high blood sugar, can also negatively impact productivity. Symptoms include increased thirst, frequent urination, and fatigue. Over time, chronic hyperglycemia can lead to long-term complications. These include damage to the eyes, kidneys, and nerves. In the short term, hyperglycemia can cause decreased concentration and lethargy. This can make it difficult to focus on tasks and maintain a high level of performance. Effective management of hyperglycemia involves medication, diet, and lifestyle adjustments.
Strategies for Managing Diabetes at Work
Successfully managing diabetes in the workplace requires a multi-faceted approach. This includes proactive planning, open communication, and a commitment to self-care. By implementing the following strategies, individuals with diabetes can maintain their health and productivity.
Planning and Preparation
Planning is key to managing diabetes effectively. This includes meal planning, medication management, and regular blood sugar monitoring. Individuals should develop a meal plan that aligns with their medication schedule and activity levels. They should also ensure they have access to healthy snacks at work. Regular blood sugar monitoring is crucial for tracking glucose levels. This allows for timely adjustments to medication or diet. Keeping a log of blood sugar readings and any related symptoms can help identify patterns and triggers. This information is valuable when consulting with a healthcare provider.
Open Communication and Workplace Support
Open communication with employers and colleagues is essential. This is to ensure a supportive work environment. Individuals with diabetes should inform their employer about their condition. This allows them to request necessary accommodations. These might include flexible break times for blood sugar monitoring or medication administration. It’s also important to educate colleagues about diabetes. This helps to dispel misconceptions and foster understanding. Creating a supportive network at work can significantly reduce stress. This can make it easier to manage diabetes. [See also: Workplace accommodations for medical conditions]
Healthy Lifestyle Choices
Adopting a healthy lifestyle is vital for managing diabetes. This includes regular physical activity, a balanced diet, and stress management techniques. Regular exercise can improve insulin sensitivity and help regulate blood sugar levels. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise per week. This can include activities like brisk walking, swimming, or cycling. A balanced diet, rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, is essential. Limit processed foods, sugary drinks, and saturated fats. Stress can significantly impact blood sugar levels. Practicing stress management techniques, such as meditation or deep breathing, can be beneficial. Adequate sleep is also crucial for overall health and diabetes management.
Practical Tips for the Workplace
Implementing practical tips can make managing diabetes at work easier. These tips focus on specific aspects of the workday. They aim to minimize disruptions and maximize productivity.
Meal and Snack Planning
Plan meals and snacks in advance. This will help to maintain stable blood sugar levels. Pack healthy snacks, such as fruits, vegetables, or nuts. This ensures you have options available. Avoid sugary drinks and processed foods, which can cause blood sugar spikes. Schedule meals and snacks at consistent times throughout the day. This helps to regulate insulin and glucose levels. If working late, plan for extra snacks to prevent hypoglycemia.
Medication Management
Keep medication readily accessible. Store it in a safe and convenient place. Follow the prescribed medication schedule. Take medication as directed by your healthcare provider. If using insulin, ensure proper storage and handling. Have a backup plan in case of medication emergencies. Carry a list of your medications and dosages. This information is helpful in case of a medical emergency. Consider using a medication reminder app to stay on track.
Blood Sugar Monitoring
Monitor blood sugar levels regularly throughout the day. This allows for timely intervention. Keep a blood glucose meter and supplies readily available. Test blood sugar before meals, before and after exercise, and before bedtime. Record blood sugar readings and any related symptoms. Share this information with your healthcare provider. Learn to recognize the symptoms of high and low blood sugar. This allows for prompt action. Adjust medication or diet as needed, based on blood sugar readings and healthcare provider guidance.
Addressing Workplace Stress
Stress can significantly impact blood sugar levels. Identify stressors in the workplace. This allows for proactive management. Take short breaks throughout the day to de-stress. Practice deep breathing exercises or meditation. Communicate with your supervisor about any excessive workload or deadlines. Seek support from colleagues or a therapist. Engage in activities that you find relaxing and enjoyable. This helps to reduce overall stress levels.
Seeking Professional Support
Managing diabetes effectively requires professional guidance. This includes consulting with healthcare providers, diabetes educators, and nutritionists. Regular check-ups with a physician are essential for monitoring overall health and managing diabetes. A diabetes educator can provide education and support. They can teach you how to manage your condition. A registered dietitian can help you develop a personalized meal plan. This plan will help to optimize blood sugar control. Don’t hesitate to seek help from these professionals. They can provide valuable insights and support.
Conclusion: Thriving with Diabetes at Work
Managing diabetes in the workplace is achievable with the right strategies. By planning ahead, communicating openly, and adopting a healthy lifestyle, individuals can maintain their health. They can also sustain their productivity. Remember that diabetes does not have to be a barrier to professional success. With proactive management, individuals with diabetes can thrive in their careers. They can achieve their professional goals. The key is to be informed, proactive, and supported. This ensures a healthy and productive work life. [See also: Diabetes management resources]
Diabetes at work is manageable. It is essential to prioritize your health. Understanding the challenges of diabetes and implementing the strategies outlined in this article can significantly impact your success. With dedication and support, you can maintain optimal health and achieve your professional goals. Remember to consult with your healthcare provider. They can provide personalized guidance. This ensures you manage your diabetes effectively.