How to Lower Diabet A1C Levels in Just a Few Simple Steps
Managing diabetes can feel like navigating a complex maze. The constant monitoring, the dietary restrictions, and the medications can be overwhelming. However, achieving optimal control over your blood sugar levels, particularly your A1C, doesn’t have to be an insurmountable challenge. In fact, with a few simple steps, you can significantly improve your A1C and overall health. This article delves into practical, evidence-based strategies on how to lower Diabet A1C levels, empowering you to take control of your health journey.
Understanding A1C and Its Significance
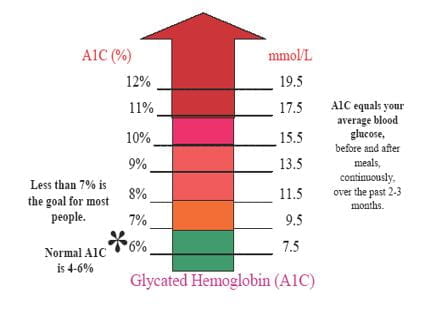
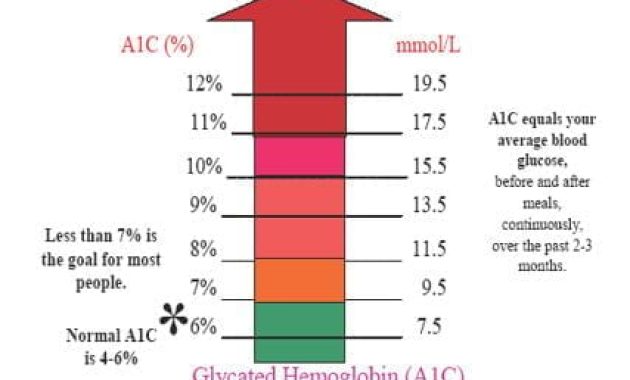
Before we explore the methods to lower A1C, it’s crucial to grasp what it is and why it matters. A1C, or glycated hemoglobin, is a blood test that reflects your average blood sugar levels over the past two to three months. It measures the percentage of hemoglobin (a protein in red blood cells) that has glucose attached to it. A higher A1C indicates higher average blood sugar levels, increasing the risk of diabetes-related complications.
The American Diabetes Association (ADA) recommends an A1C goal of below 7% for most adults with diabetes. However, the ideal A1C target is individualized, considering factors such as age, overall health, and the risk of hypoglycemia (low blood sugar). Regular A1C testing is vital for monitoring diabetes management and assessing the effectiveness of treatment plans.
Dietary Modifications: The Cornerstone of A1C Control
Diet plays a pivotal role in managing diabetes and lowering A1C. Making informed food choices can significantly impact your blood sugar levels and overall health. Here are some key dietary strategies:
- Prioritize Fiber-Rich Foods: Fiber slows down the absorption of sugar, preventing rapid spikes in blood sugar. Include plenty of non-starchy vegetables, fruits, and whole grains in your diet.
- Control Carbohydrate Intake: Be mindful of your carbohydrate intake, as carbohydrates have the most significant impact on blood sugar. Work with a healthcare professional or a registered dietitian to determine the appropriate carbohydrate intake for your individual needs.
- Choose Healthy Fats: Opt for unsaturated fats, such as those found in avocados, nuts, seeds, and olive oil. These fats can improve insulin sensitivity and support heart health.
- Limit Processed Foods and Added Sugars: Processed foods, sugary drinks, and excessive added sugars can quickly elevate blood sugar levels. Minimize your consumption of these items.
- Focus on Portion Control: Even healthy foods can contribute to elevated blood sugar if consumed in excess. Pay attention to portion sizes and practice mindful eating.
Implementing these dietary changes can be a significant step in learning how to lower Diabet A1C levels. [See also: The Best Foods to Eat for Lowering Blood Sugar]
The Power of Physical Activity
Regular physical activity is another crucial element in managing diabetes and lowering A1C. Exercise enhances insulin sensitivity, allowing your body to utilize glucose more effectively. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity aerobic exercise per week, spread throughout the week. Incorporate strength training exercises at least two days per week.
Choose activities you enjoy to make exercise a sustainable part of your routine. This could include brisk walking, swimming, cycling, dancing, or any other activity that elevates your heart rate. Consult your healthcare provider before starting any new exercise program, especially if you have any underlying health conditions. Regular physical activity is a powerful tool in the quest of how to lower Diabet A1C levels.
Medication Management: Working with Your Healthcare Provider
For many individuals with diabetes, medication is essential to manage blood sugar levels effectively. Work closely with your healthcare provider to develop a medication plan that is tailored to your individual needs. This may involve oral medications, insulin injections, or a combination of both.
Follow your healthcare provider’s instructions carefully regarding medication dosage, timing, and administration. Regularly monitor your blood sugar levels as directed and report any concerns or side effects to your healthcare provider. Medication plays a key role in how to lower Diabet A1C levels, and should be used in accordance with your doctor’s instructions.
Stress Management and Sleep: Often Overlooked But Essential
Chronic stress and inadequate sleep can negatively impact blood sugar control. Stress hormones can raise blood sugar levels, while poor sleep can disrupt insulin sensitivity. Prioritize stress management techniques, such as meditation, yoga, deep breathing exercises, or spending time in nature. Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep per night.
Create a relaxing bedtime routine and establish a consistent sleep schedule. If you are struggling with stress or sleep, consider seeking professional help from a therapist or sleep specialist. These lifestyle adjustments can subtly influence how to lower Diabet A1C levels.
Regular Monitoring and Follow-up: Staying on Track
Regular blood sugar monitoring is crucial for tracking your progress and making necessary adjustments to your treatment plan. Use a blood glucose meter to check your blood sugar levels as directed by your healthcare provider. Keep a log of your readings and share them with your provider at your appointments. Be sure to discuss how to lower Diabet A1C levels with your doctor during these appointments.
Attend all scheduled appointments with your healthcare provider, including your endocrinologist, primary care physician, and any other specialists involved in your care. These appointments provide opportunities to review your A1C results, discuss any challenges you are facing, and make necessary adjustments to your treatment plan. Regular check-ups are the best way to guarantee how to lower Diabet A1C levels.
Practical Tips to Implement Today
Here are some practical tips to get you started on your journey of how to lower Diabet A1C levels:
- Start Small: Don’t try to overhaul your entire lifestyle overnight. Begin by making small, manageable changes, such as adding more vegetables to your meals or going for a short walk each day.
- Set Realistic Goals: Set achievable goals that you can realistically maintain. Celebrate your successes along the way to stay motivated.
- Seek Support: Join a diabetes support group or connect with others who are managing diabetes. Sharing your experiences and learning from others can be incredibly helpful.
- Educate Yourself: Learn as much as you can about diabetes, its management, and the strategies that can help you lower your A1C.
- Be Patient: Lowering your A1C takes time and effort. Don’t get discouraged if you don’t see results immediately. Stay consistent with your efforts, and you will eventually see progress.
By implementing these simple steps and prioritizing your health, you can take control of your diabetes and improve your A1C levels. Remember, it’s a journey, not a destination. Stay committed to your health, and celebrate your progress along the way. This article gives you the knowledge of how to lower Diabet A1C levels to help you get started.
Frequently Asked Questions
How quickly can I lower my A1C?
The timeline for lowering your A1C varies depending on several factors, including your current A1C level, the strategies you implement, and your individual response to those strategies. However, with consistent effort, you can typically see improvements in your A1C within a few months. Significant improvements are expected when you learn how to lower Diabet A1C levels.
Can I lower my A1C without medication?
In some cases, lifestyle modifications alone can be sufficient to lower A1C. However, for many individuals, medication is necessary to achieve optimal blood sugar control. Work closely with your healthcare provider to determine the best approach for your individual needs.
What are the risks of high A1C?
High A1C levels increase the risk of several diabetes-related complications, including heart disease, stroke, kidney disease, nerve damage, and vision loss. Maintaining good blood sugar control is essential for preventing these complications.
How often should I check my A1C?
Your healthcare provider will determine how often you should check your A1C. Typically, A1C is checked every three to six months. It is very important to know how to lower Diabet A1C levels and keep it under control.
Is it possible to reverse diabetes?
While there is no cure for diabetes, it is possible to put type 2 diabetes into remission through lifestyle modifications, such as significant weight loss and increased physical activity. However, this requires a sustained commitment to healthy habits.
Can I eat fruit if I have diabetes?
Yes, you can eat fruit if you have diabetes. However, it’s important to choose fruits with a lower glycemic index and to consume them in moderation. Pair fruit with protein or healthy fats to help slow down the absorption of sugar.