How to Prevent Diabetes From Getting Worse: Steps to Take This Week
The diagnosis of diabetes can be a life-altering moment. It often brings a mix of emotions: fear, confusion, and a determination to take control. The good news is that diabetes, while chronic, is manageable. You have the power to significantly influence its progression. This article focuses on actionable steps you can begin implementing this week to prevent diabetes from worsening. We’ll explore lifestyle changes, medical considerations, and resources to help you navigate this journey.
Understanding Diabetes and Its Progression
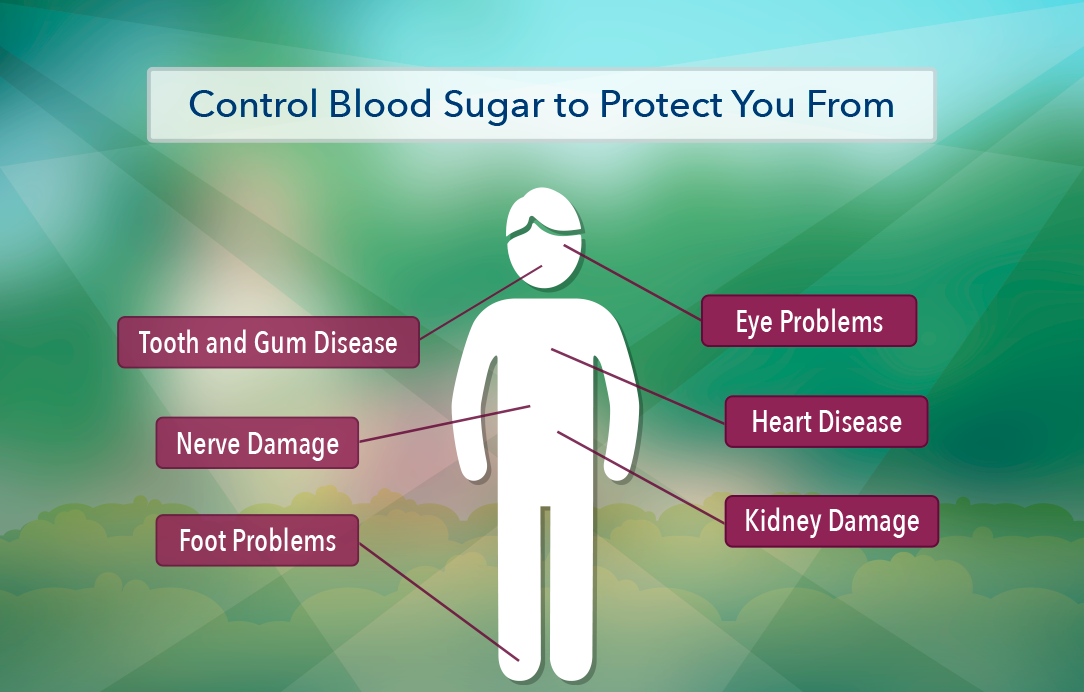
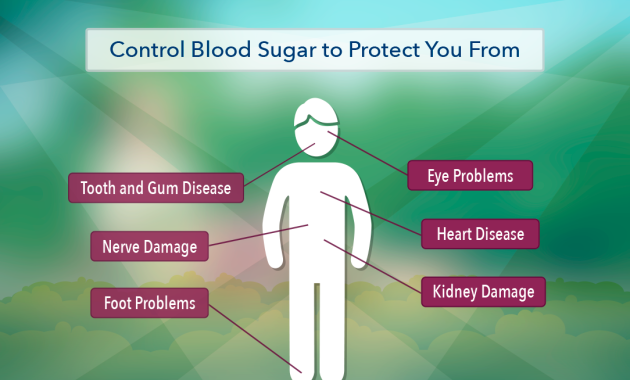
Diabetes is a metabolic disorder characterized by elevated blood sugar levels. This occurs when the body either doesn’t produce enough insulin or can’t effectively use the insulin it produces. Insulin is a hormone that regulates blood sugar. Over time, uncontrolled high blood sugar can lead to serious health complications. These include heart disease, kidney failure, nerve damage (neuropathy), and vision loss. Understanding the disease and its potential impact is the first step in effective management.
There are several types of diabetes. Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune disease where the body attacks the insulin-producing cells in the pancreas. Type 2 diabetes is the most common type. It often develops over time, frequently linked to lifestyle factors such as diet and lack of exercise. Prediabetes is a condition where blood sugar levels are higher than normal but not yet high enough to be diagnosed as type 2 diabetes. Addressing prediabetes is critical for preventing the onset of full-blown diabetes.
Dietary Changes to Stabilize Blood Sugar
Diet plays a crucial role in managing diabetes and preventing it from getting worse. The goal is to control blood sugar levels through mindful eating. This involves making informed choices about the foods you consume. Start this week by focusing on these key dietary adjustments:
- Prioritize Complex Carbohydrates: Choose whole grains, vegetables, and fruits over refined carbohydrates like white bread, pasta, and sugary cereals. These complex carbohydrates are digested more slowly. They provide a steadier release of glucose into the bloodstream.
- Control Portion Sizes: Be mindful of the amount of food you eat at each meal. Overeating can lead to blood sugar spikes. Use smaller plates and measure your food to get a better understanding of portion sizes.
- Increase Fiber Intake: Fiber helps slow down the absorption of sugar. It also promotes feelings of fullness. Include plenty of non-starchy vegetables, such as broccoli, spinach, and green beans, in your meals.
- Choose Lean Proteins: Protein helps stabilize blood sugar levels. It also keeps you feeling full. Opt for lean protein sources like fish, poultry, beans, and tofu.
- Limit Added Sugars: Avoid sugary drinks, processed foods, and excessive amounts of added sugar. Read food labels carefully to identify hidden sugars.
- Focus on Healthy Fats: Choose healthy fats like those found in avocados, nuts, and olive oil. Limit saturated and trans fats.
The Importance of Regular Physical Activity
Physical activity is another powerful tool for managing diabetes. Exercise helps improve insulin sensitivity, enabling the body to use insulin more effectively. It also helps lower blood sugar levels. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise per week, or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity exercise. This can be broken down into shorter sessions throughout the week.
Consider these exercise tips:
- Find Activities You Enjoy: This will make it easier to stick to your exercise routine. Consider walking, swimming, cycling, or dancing.
- Start Slowly and Gradually Increase Intensity: If you’re new to exercise, begin with short walks and gradually increase the duration and intensity.
- Incorporate Strength Training: Strength training helps build muscle mass, which can improve insulin sensitivity.
- Monitor Blood Sugar Levels: Before and after exercise, check your blood sugar levels. This helps you understand how your body responds to physical activity.
- Consult Your Doctor: Before starting any new exercise program, consult your doctor, especially if you have any underlying health conditions.
Medication and Medical Management
For many people with diabetes, medication is necessary to manage blood sugar levels. Work closely with your healthcare provider to develop a medication plan that’s right for you. This may involve oral medications or insulin injections. Never adjust your medication dosage without consulting your doctor. Regular check-ups and monitoring are essential. This allows your doctor to assess your progress and make any necessary adjustments to your treatment plan.
Here are some key aspects of medical management:
- Regular Blood Sugar Monitoring: Monitor your blood sugar levels as directed by your doctor. This provides valuable information about how your body responds to food, exercise, and medication.
- A1C Testing: Get your A1C levels checked regularly. This test measures your average blood sugar levels over the past two to three months.
- Foot Care: People with diabetes are at increased risk of foot problems. Inspect your feet daily for any cuts, blisters, or sores.
- Eye Exams: Schedule regular eye exams to check for any signs of diabetic retinopathy (damage to the blood vessels in the retina).
- Kidney Function Tests: Get your kidney function checked regularly to monitor for any signs of diabetic nephropathy (kidney damage).
- Vaccinations: Stay up-to-date on recommended vaccinations, such as the flu shot and pneumonia vaccine.
Stress Management and Mental Health
Stress can significantly impact blood sugar levels. Managing stress is an important part of diabetes management. Stress hormones can cause blood sugar to rise. Find healthy ways to cope with stress. This might include exercise, relaxation techniques, or spending time with loved ones.
Consider these stress-reduction strategies:
- Practice Relaxation Techniques: Try deep breathing exercises, meditation, or yoga.
- Get Enough Sleep: Aim for seven to eight hours of sleep per night.
- Engage in Hobbies: Make time for activities you enjoy, such as reading, gardening, or listening to music.
- Connect with Others: Talk to friends, family, or a therapist.
- Seek Professional Help: If you’re struggling with stress or anxiety, consider seeking help from a mental health professional.
Building a Support System
Managing diabetes can be challenging. Having a strong support system can make a big difference. This could include family, friends, or a diabetes support group. Sharing your experiences and connecting with others who understand what you’re going through can be incredibly helpful. Your healthcare team is also an important part of your support system. Don’t hesitate to ask questions and seek guidance from your doctor, nurse, or diabetes educator.
Steps to Take This Week
Now, let’s focus on how to prevent diabetes from getting worse starting this week. Here’s a practical action plan:
- Schedule a Doctor’s Appointment: If you haven’t already, schedule an appointment with your doctor. Discuss your diabetes management plan.
- Review Your Diet: Take a close look at your current diet. Identify areas where you can make healthier choices. Start by planning your meals for the next few days.
- Plan Your Meals: Create a meal plan for the week. This will help you make healthier food choices.
- Start Moving: Incorporate at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise into your daily routine. It could be a brisk walk, cycling, or other activities.
- Check Blood Sugar Levels: Monitor your blood sugar levels regularly. This will give you valuable insights into how your body responds to food and exercise.
- Join a Support Group: Consider joining a diabetes support group. This will help you connect with others who understand what you’re going through.
- Educate Yourself: Read reliable information about diabetes management. Understanding the condition empowers you to take control.
Long-Term Commitment and Lifestyle Changes
Preventing diabetes from worsening is a long-term commitment. It requires consistent effort and dedication. There will be times when you face challenges. However, it’s important to stay focused on your goals. The lifestyle changes you make today will have a significant impact on your health. They will help you prevent diabetes from getting worse. Remember, you are not alone. There are many resources available to support you on your journey.
Diabetes management is a continuous process. It’s about making informed choices and staying proactive. By taking these steps this week and continuing to make healthy lifestyle choices, you can significantly improve your health and well-being. You can prevent diabetes from getting worse. You can live a full and active life with diabetes. [See also: Managing Diabetes During the Holidays] [See also: The Role of Exercise in Diabetes Management]
If you have any concerns about how to prevent diabetes from getting worse, seek advice from your healthcare provider. They can provide personalized guidance. They can tailor it to your specific needs and circumstances. Remember that every step you take, no matter how small, is a step in the right direction. Your commitment to managing your diabetes will pay off in the long run. You can live a healthier, happier life.
The strategies discussed in this article are designed to help people with diabetes. These can help prevent diabetes from getting worse. They are not a substitute for medical advice. Always consult your doctor or other qualified healthcare provider. They can provide guidance for your individual medical needs.
Remember, with the right knowledge and commitment, you can take control. You can prevent diabetes from getting worse. You can improve your quality of life. Taking action this week is a crucial step in the right direction. Your health is an investment worth making.